
Elements in column 14, the second column of the p-block, have two p-orbital electrons. Elements in column 13, the first column of the p-block, have one p-orbital electron. The p orbital can hold a maximum of six electrons, hence there are six columns in the p-block.
The p orbital consists of six lobed shapes coming from a central point at evenly spaced angles. The p-block elements are unified by the fact that their valence (outermost) electrons are in the p orbital.
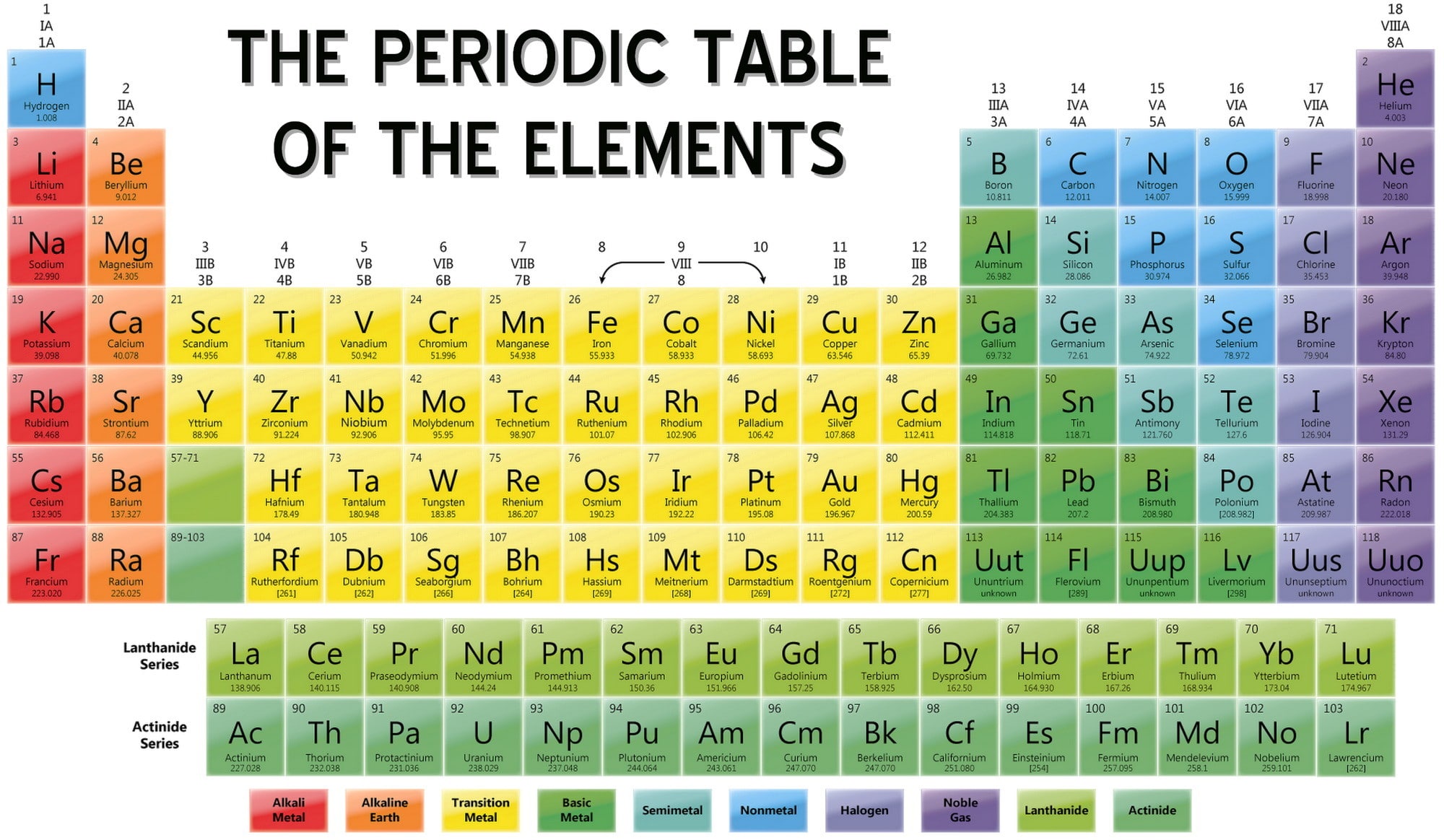
Alternatively, the p-block can be described as containing post-transition metals metalloids reactive nonmetals including the halogens and noble gases (excluding helium). The p-block elements can be described on a group-by-group basis as: group 13, the icosagens 14, the crystallogens 15, the pnictogens 16, the chalcogens 17, the halogens and 18, the helium group, composed of the noble gases (excluding helium) and oganesson. This block is the only one having all three types of elements: metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Each row of the table has a place for six p-elements except for the first row (which has none). Helium, though being the first element in group 18, is not included in the p-block. Their general electronic configuration is ns 2 np 1–6. The p-block, with the p standing for "principal" and azimuthal quantum number 1, is on the right side of the standard periodic table and encompasses elements in groups 13 to 18. Metals of the s-block are highly electropositive and often form essentially ionic compounds with nonmetals, especially with the highly electronegative halogen nonmetals. Most impart colour to a flame.Ĭhemically, all s-elements except helium are highly reactive. The metals of the s-block (from the second period onwards) are mostly soft and have generally low melting and boiling points. Each row of the table has two s-elements. Helium is an s-element, but nearly always finds its place to the far right in group 18, above the p-element neon. Their general valence configuration is ns 1–2.
#C element periodic table plus#
The s-block, with the s standing for "sharp" and azimuthal quantum number 0, is on the left side of the conventional periodic table and is composed of elements from the first two columns plus one element in the rightmost column, the nonmetals hydrogen and helium and the alkali metals (in group 1) and alkaline earth metals (group 2). The role of calcium and comparable cations in animal behaviour, RSC, Cambridge, p. This enables …ions to move around the cell without…danger of being oxidised or reduced. Sr…These metals display only one stable oxidation state. Li and Ba) and/or occur as minor but useful contaminants in Ca bio-minerals e.g. Some…other s-block elements are used in medicine (e.g. …Na, K, Mg and Ca are essential in biological systems.
#C element periodic table full#
Helium is an s-block element, with its outer (and only) electrons in the 1s atomic orbital, although its chemical properties are more similar to the p-block noble gases in group 18 due to its full shell. Groups (columns) in the f-block (between groups 2 and 3) are not numbered.

However, they remain d-block elements even when considered to be main group. The group 3 elements are occasionally considered main group elements due to their similarities to the s-block elements. The group 12 elements zinc, cadmium, and mercury are sometimes regarded as main group, rather than transition group, because they are chemically and physically more similar to the p-block elements than the other d-block elements. The s-block and p-block together are usually considered main-group elements, the d-block corresponds to the transition metals, and the f-block corresponds to the inner transition metals and encompasses nearly all of the lanthanides (like lanthanum) and the actinides (like actinium). There is an approximate correspondence between this nomenclature of blocks, based on electronic configuration, and sets of elements based on chemical properties. Useful statements about the elements can be made on the basis of the block they belong to and their position in it, for example highest oxidation state, density, melting point… Electronegativity is rather systematically distributed across and between blocks. The division into blocks is justified by their distinctive nature: s is characterized, except in H and He, by highly electropositive metals p by a range of very distinctive metals and non-metals, many of them essential to life d by metals with multiple oxidation states f by metals so similar that their separation is problematic.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
